Match the Possible Consequence of Drug Metabolism to Its Example.
3- Appraisal of drugs therapeutic side and adverse effects. The amount of absorption helps determine how intense effects will be.

Chapter 5 Pharmacokinetics Drugs And Behavior
Drug metabolism is the term used to describe the biotransformation of pharmaceutical substances in the body so that they can be eliminated more easily.

. The primary objective of drug metabolism is to facilitate a drugs excretion by increasing its water solubility hydrophilicity. Provision of Drug information. Match with these Right Evaluation Right Education Right Assessment Right Documentation.
O Metabolism Metabolism or biotransformation is the process by which the body chemically changes drugs into a form that can be excreted. For example if rifampin is taken concomitantly with imatinib imatinibs plasma concentrations can be reduced because rifampin can induce CYP3A4 activity. The level of these cytochrome P-450.
This classfication is an example of what typer of. Conversely an increased rate of metabolism decreases the intensity and duration of action as well as the drugs efficacy. Demonstrate that the metabolism of a drug is a primary concern throughout its lifetime from its inception chemical design and optimisation to its final clinical use and that for any given drug the multiple factors influencing its metabolism necessitate on-going studies of its biotransformation.
For example if 500 mg is present in the body at time zero after metabolism 250 mg may be present at 1 hour and 125 mg at 2 hours illustrating a half-life of 1 hour. What is the purpose of instrument calibration. Terms in this set 60 toprol is the brand name for what medication.
Must convert from lipid-soluble into hydrophilic water-soluble molecules. For example NAM by itself inhibits polyADP-ribose polymerases PARPs which protect genome integrity. Some drugs introduced into the alimentary tract are absorbed directly into the systemic circulation without passing through the liver eg.
Thus imatinibs anticancer activity can be attenuated. Via the buccal sublingual or rectal routes thereby avoiding the potential hazards of gastric acid binding to food and metabolism by gut wall or liver enzymes first-pass metabolism. The livers primary mechanism for metabolizing drugs is via a specific group of cytochrome P-450 enzymes.
This procedure where the drug is converted to a metabolite is called biotransformation and they are classified as Phase I functionalization reactions and Phase II junction reactions. Once in the liver enzymes convert prodrugs to active metabolites or convert active drugs to inactive forms. 4- Patients has remained free of injury.
Some drugs eg metoclopramide increase gastrointestinal motility decreasing food absorption. 2 Effects of Age. The above hypothetical case is a good example of the requirement to consider chiral-selective metabolism and its potential implications on pharmacodynamics PK toxicology and bio-analytical.
Of codeine into morphine by CYP2D6. Many drugs affect appetite food absorption and tissue metabolism see table Effects of Some Drugs on Appetite Food Absorption and Metabolism. Some drugs are better tolerated if taken.
This in turn provides information regarding a drugs appropriate use possible side effects and possible contraindications. Drug metabolism can affect the plasma concentrations of drugs. Most drugs must pass through the liver which is the primary site for drug metabolism.
Effects of Age on Drug Metabolism. Match the right to its example. Patient is alert and oriented.
In addition decreased metabolic elimination may lead to accumulation of toxic levels of the drug. For example prescribers need to be concerned about drug-drug interactions. -the MOST important consequence of drug metabolism is promotion of renal drug excretion -kidney is unable to excrete drugs that are highly lipid- soluble.
It is a warning placed on certain drugs of potential hazards associated with taking the drug. Metabolism is related to SA not body weight. 1- Collection of appropriate data after drug administration.
High-level NAM administration can exert negative effects through multiple routes. However possible adverse effects and their mechanisms are poorly understood. - children have metabolism that is higher than weight.
In such cases called first-order elimination or kinetics the metabolism rate of the drug is a constant fraction of the drug remaining in the body ie the drug has a specific half-life. The terminal consequence of drug metamorphosis is to extinguish the drug from the organic structure as either unchanged signifier or through transition to metabolites. To ensure the accuracy of its measurement.
Elevation of the NAD pool alters cellular energy metabolism. O Distribution Distribution is drug movement from the blood to the tissues and into the cells. Other drugs eg opioids anticholinergics decrease gastrointestinal motility.
Drugs can be metabolized by oxidization decrease hydrolysis hydration junction condensation or isomerisation whatever the procedure the end is to do the drug easier to egest. - elderly have a reduced metabolism. The majority of metabolic processes that.
For example if the rate of metabolism of a drug is decreased this generally increases the intensity and duration of the drug action. The enzymes involved in metamorphosis are present in many tissues but by and large are more concentrated in the liver. - teensadults have metabolic rate proportional to body size.
The involved chemical modifications incidentally decrease or increase a drugs pharmacological activity andor half-life the most extreme example being the metabolic activation of inactive prodrugs into active drugs eg.

Chapter 5 Pharmacokinetics Drugs And Behavior
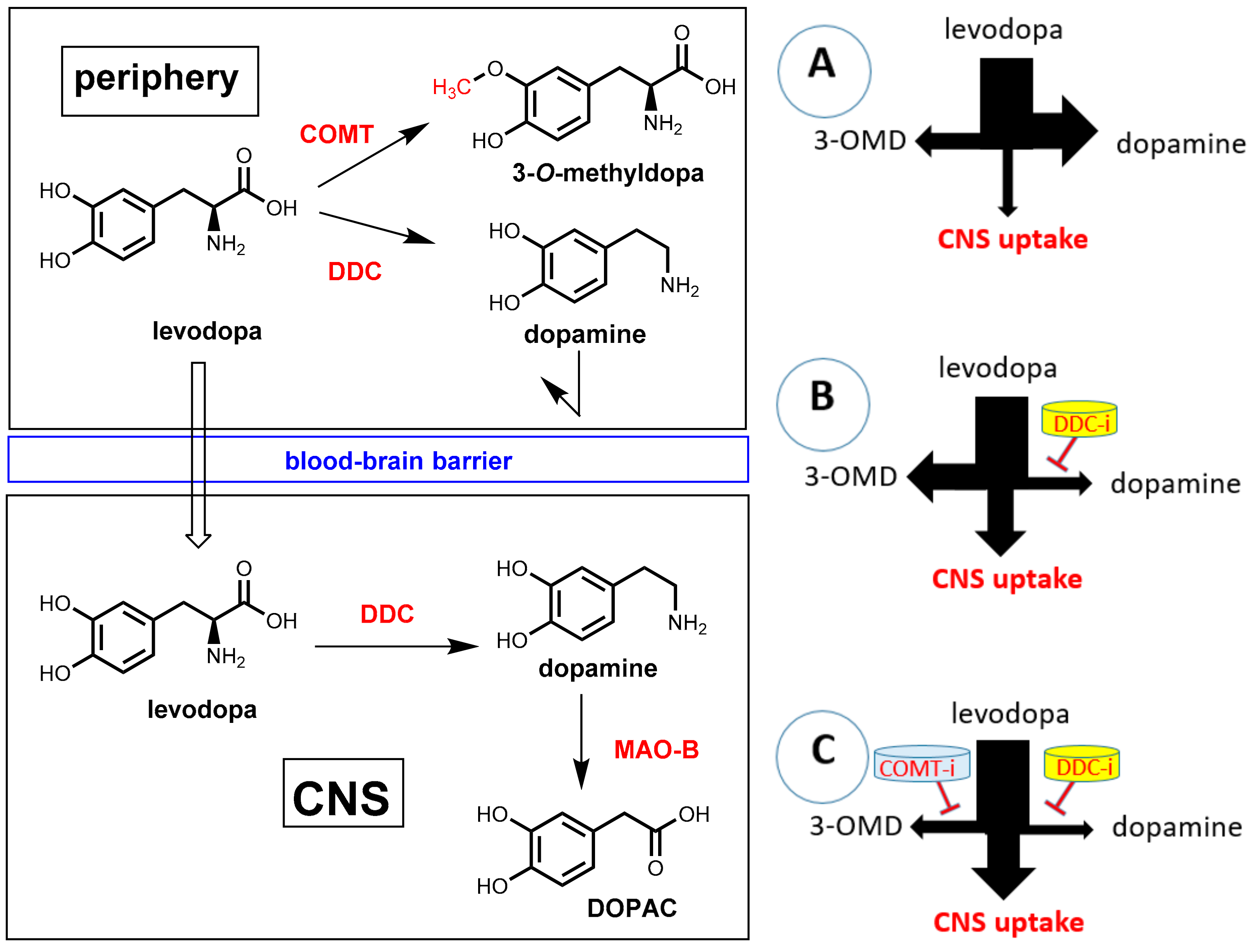
Sci Pharm Free Full Text Pharmacokinetic Enhancers Boosters Escort For Drugs Against Degrading Enzymes And Beyond Html

Database For Drug Metabolism And Comparisons Nicedrug Ch Aids Discovery And Design Biorxiv

Drug Metabolism And Variability Among Patients In Drug Response Nejm

Rare Variation In Drug Metabolism And Long Qt Genes And The Genetic Susceptibility To Acquired Long Qt Syndrome Circulation Genomic And Precision Medicine

Drug Receptor Interactions An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Advance On The Absorption Metabolism And Efficacy Exertion Of Quercetin And Its Important Derivatives Hai 2020 Food Frontiers Wiley Online Library

Food For Thought Formulating Away The Food Effect A Pearrl Review O Shea 2019 Journal Of Pharmacy And Pharmacology Wiley Online Library
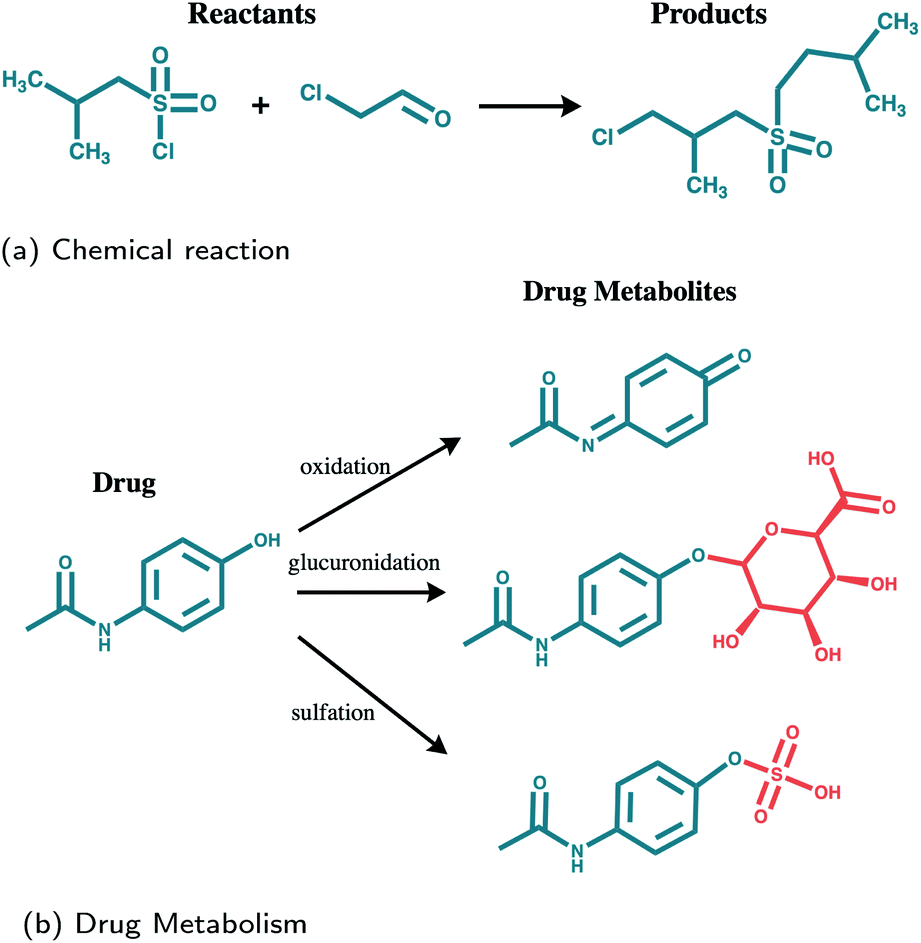
Prediction Of Drug Metabolites Using Neural Machine Translation Chemical Science Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 D0sc02639e

Cholesterol Lowering Drugs Endotext Ncbi Bookshelf

First Pass Metabolism Nurse Prescribing

Drug Metabolism 1 Flashcards Quizlet
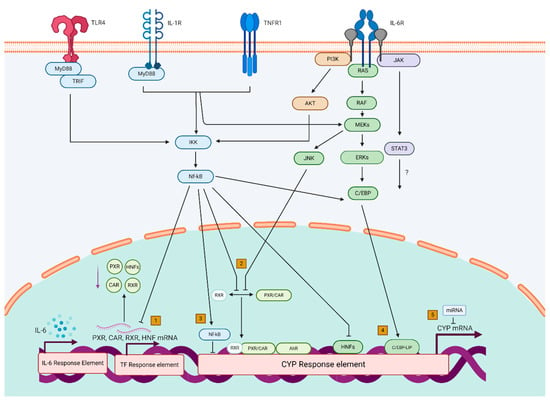
Genes Free Full Text Distinct Effects Of Inflammation On Cytochrome P450 Regulation And Drug Metabolism Lessons From Experimental Models And A Potential Role For Pharmacogenetics Html

Chromosomal Instability And Aneuploidy As Causes Of Cancer Drug Resistance Trends In Cancer

How Do Cells Cope With Rna Damage And Its Consequences Journal Of Biological Chemistry

Frontiers In Pharmacology Drug Metabolism And Transport

Clinical Studies On Drug Drug Interactions Involving Metabolism And Transport Methodology Pitfalls And Interpretation Tornio 2019 Clinical Pharmacology Amp Therapeutics Wiley Online Library

Comments
Post a Comment